The aim of this study was to identify the methods most commonly used for monitoring vaccination-related topics on different…


The aim of this study was to identify the methods most commonly used for monitoring vaccination-related topics on different…
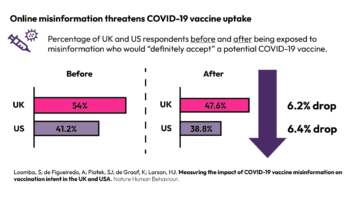
To inform successful vaccination campaigns, we conducted a randomized controlled trial in the UK and…

This study aims to assess global hesitancy, confidence, and public engagement toward COVID-19 vaccination.

This study was a comparative analysis between the United Kingdom and China, which…

In this large-scale retrospective data-driven analysis, we examined global trends in vaccine…
This article investigates how hope and trust played…

This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis to examine the strength of the relationships between…

Book chapter exploring how to communicate about the benefits and risks of vaccination in times of pandemics and uncertainties.

Introducing The Lancet–London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine Commission.

Within weeks of the emergence of the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China, misleading rumours and conspiracy theories about the origin circulated the globe paired with fearmongering, racism and mass purchase of face masks, all closely linked to the new ‘infomedia’ ecosystems of the 21st century marked by social media.

The Vaccine Confidence Project™ conducted a systematic scoping review to identify and summarise tools and methodologies that have been used to monitor social media around vaccination.

This systematic review aims to identify the social consequences of mass quarantine during previous and current infectious disease outbreaks and recommended strategies to mitigate the negative social implications of COVID-19 lockdowns.